Multiple Sexual Partners and HPV: What Every Man Should KnowIn today’s age of sexual freedom and evolving relationship dynamics, conversations around sexual health are more important than ever. While casual relationships are increasingly normalized, the risks tied to them—especially the human papillomavirus (HPV)—are often overlooked.This article explores how having multiple female partners can increase the likelihood of HPV transmission in men, what HPV is, why it matters for male health, and the steps one can take to stay protected. With HPV being one of the most common sexually transmitted infections (STIs) globally, the discussion is not just relevant—it’s critical.
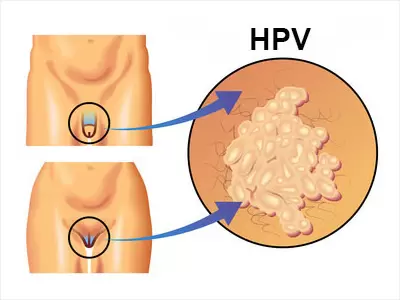
What Is HPV and Why Should Men Be Concerned?Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a group of over 200 related viruses, with at least 40 of them transmitted through direct sexual contact.
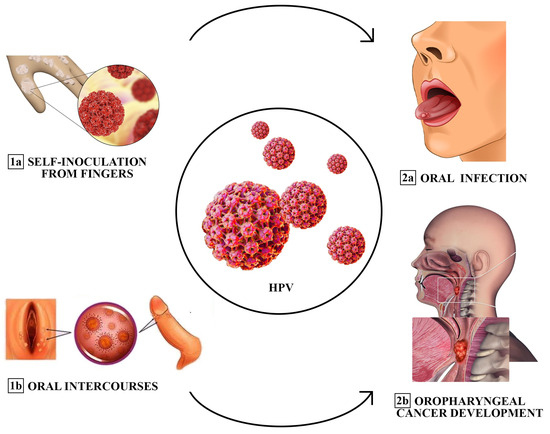
While some strains are harmless and clear up on their own, others can lead to serious health issues.In women, HPV is widely known for its link to cervical cancer. However, men are not immune to the consequences of HPV. The virus can cause genital warts and, in some cases, lead to cancers of the throat, anus, and penis.The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that nearly all sexually active individuals will contract HPV at some point in their lives. For men who have multiple female partners, the risk increases substantially due to greater exposure to the virus. How Is HPV Transmitted?
HPV spreads primarily through skin-to-skin contact during vaginal, anal, or oral sex. Unlike infections that require bodily fluids for transmission, HPV can pass even without penetration. That means condoms, while helpful, do not offer full protection against it.It’s also possible to contract HPV from someone who shows no symptoms. Since many HPV infections are asymptomatic, a partner can unknowingly transmit the virus. This silent spread makes it particularly difficult to detect early unless regular screenings are done.